Tonsils and Adenoids
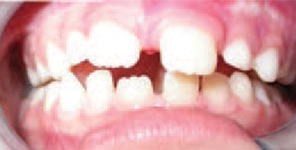
The tonsils and adenoids are part of the immune system in children. Adenoids are situated in the posterior portion of the nose. Enlarged tonsils and adenoids reduced or prevent nasal breathing, proper function of the soft palate and middle ear and may cause OSA.
OMT
HELPS
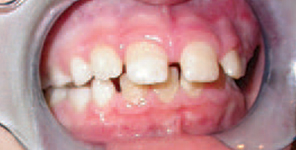
Enlarged tonsils and adenoids are to be suspected when there is an open mouth posture; tongue thrust, painful swallowing, nasal voice and other possible signs. A referral to an ENT is recommended as enlarged tonsils and adenoids (not visible from the mouth) are a medical condition that needs to be addressed medically.
IF NOT
TREATED
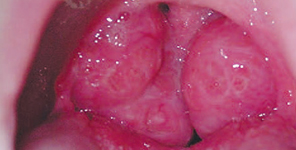
Enlarged tonsils may lead to chronic open mouth posture, mouth breathing, bad breath, sleep disordered breathing, tongue thrust, dental malocclusion and some degrees of craniofacial anomalies.
Enlarged (hypertrophic) adenoids may also contribute to sleep disorders, poor nasal breathing, chronic open mouth posture, changes in voice resonance (sounding too “nasal”), ear infections and symptoms and degrees of craniofacial anomalies.

13. Tonsils and Adenoids
–Valera FC, Trawitzki LV, Anselmo-Lima WT. Myofunctional evaluation a er surgery for tonsils hypertrophy and its correlation to breathing pattern: A 2-year-follow up. International Journal of Pediatric Otorhinolaryngology (2006) 70, 221–225
–Oulis CJ, Vadiakas GP, Ekonomides J, Dratsa J. e e ect of hypertrophic adenoids and tonsils on the development of posterior crossbite and oral habits, J. Clin. Pediatr. Dent. 18 (3) (1994) 197–201.doi: 10.1590/S1807- 59322009000100007
–Linder-Aronson S. Adenoids: their e ect on mode of breathing and nasal air ow and their relationship to characteristics of the facial skeleton and the dentition. Acta Otolaryngol. Suppl. 265 (1970) 1–132.