Mouth Breathing

When the nose is congested or occluded mouth breathing is obligatory. However, often the habit of oral breathing is present even after the nasal breathing is restored.
OMT
HELPS
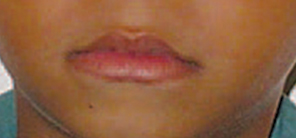
Identification of insufficient nasal breathing and proper referrals are made. Behavioral modification techniques and function re-training is implemented to change the mouth breathing habit and promote lip-together proper nasal breathing.
IF NOT
TREATED
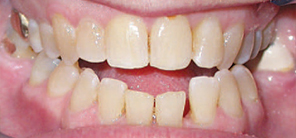
Mouth breathing is meant to be an emergency situation. When it’s chronic, a long face develops with undesirable changes to the maxilla, jaw, nose, mouth, neck and shoulders. Mouth breathing is linked to gum disease, sleep disorders, temporomandibular joint disorder behavioral issues in children, forward head posture and more.

1. Mouth breathing/nasal breathing
–Gallo J, Campiotto AR. Myofunctional therapy in 570 children with oral breathing. Rev CEFAC 2009; 11(Suppl
3):305–10. http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S1516-18462009000700005.
–Cunha DA, da Silva GA, Motta ME, et al. Mouth breathing in children and its repercussions in the nutritional
state. Rev CEFAC 2007;9(1):47–54. http:// dx.doi.org/10.1590/S1516-18462007000100007.
–Mathur R, Mortimore IL, Jan MA, Douglas NJ. Effect of breathing, pressure and posture on palatoglossal and
genioglossal tone. Clinical Science.1995. 89: 441-445.
–Bresolin D, Shapiro GG, Shapiro PA, Dassel SW, Furukawa CT, Pierson WE, Chapko M, Bierman, CW. Facial
characteristics of children who breathe through the mouth. Pediatrics. 1984. 73(5):622-5.